Deviations in shape .
- Fusion: results from the union of two adjacent tooth germs. The radiographic appearance is an unusual shape or size of crown and a root with unusual shape or multiple root canals.
- Gemination: occurs when a single tooth bud attempts to divide with result of an invagination of the crown with partial division. In rare cases complete division through the crown and root occurs, producing identical structures. The radiographic appearance is an enlarged crown containing a single or partially divided pulp chamber and an enlarged root canal. In some cases, fusion and gemination cannot be distinguished.
- Concrescence: two adjacent teeth are connected by cementum.
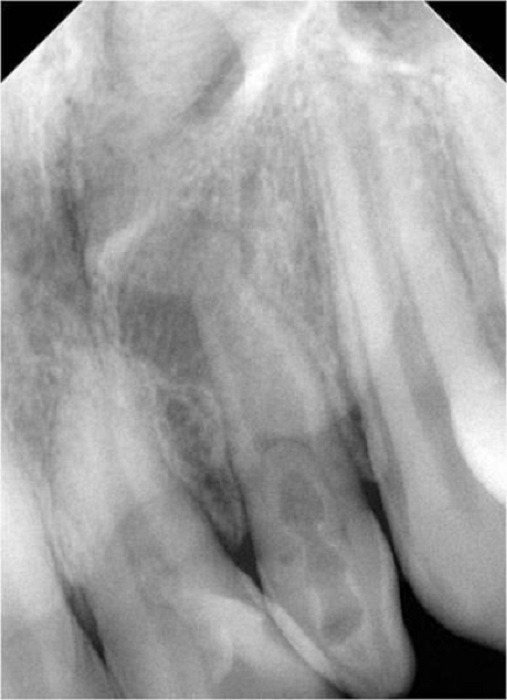
- Dens-in-dente (dens invaginatus): Results from invagination or folding of the enamel surface into the interior of a developing tooth. Most of the cases are discovered during radiographic examination and an abnormal shape of the crown is observed, containing a radiolucent area with radiopaque border, resembling tooth germ.
- Taurodontism. The roots are short and the pulp chamber is elongated leading to a more apical positioned pulpal floor.
- Dilaceration. Is a sharp bend or curve in the tooth that happens in the crown or the root.