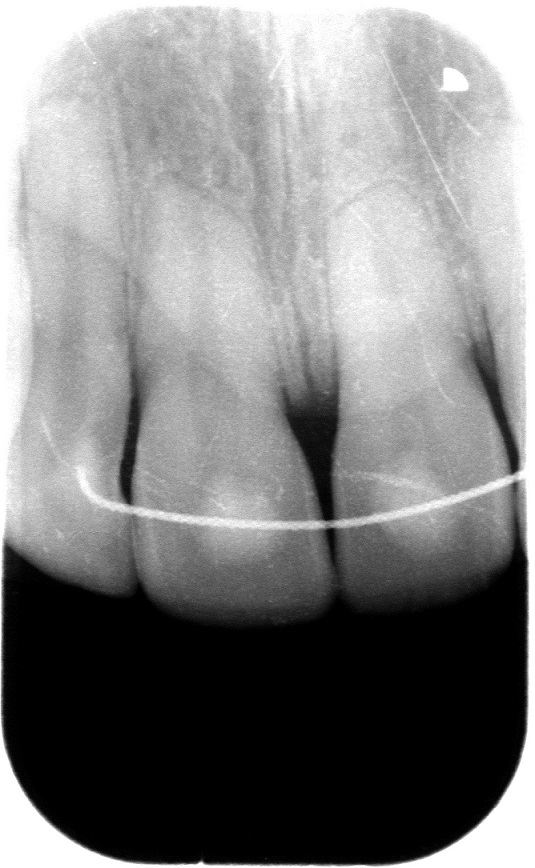
Root resorption .
- Tooth root resorption is multifactorial, leading to progressive destruction and eventual loss of tooth root dentin and cement.
- There are internal and external types of root resorption, each having its variety.
- The most significant etiological factors for external root resorption are: trauma, pressure from impacted teeth or slow-growing tumors or cysts and orthodontic treatment.
- Internal root resorption is a pathological phenomenon that can be characterized by loss of dentin due to osteoclasts. The most significant etiological factor is pulpal inflammation.