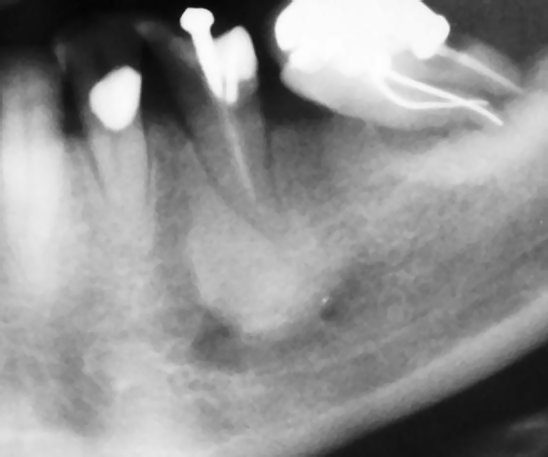
Condensing osteitis .
- It is an unusual reaction to a low-grade bacterial infection entering the bone through a carious tooth with pulpitis or a tooth with necrosis.
- Instead of bone resorption, proliferation of osseous tissue takes place.
- The sclerosing bone is not attached to the tooth and remains steady after tooth extraction. No surgical removal is needed.