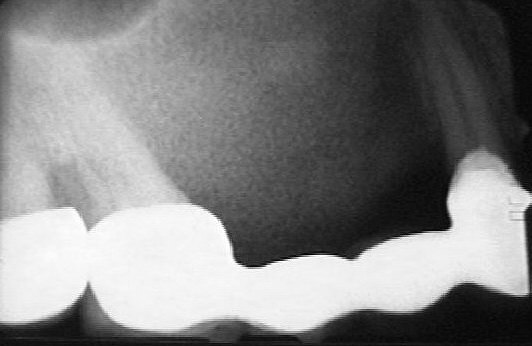
Fibrous dysplasia (radiopacity) .
- Idiopathic replacement of all the components of cancellous bone by fibrous tissue containing varying amounts of abnormal bone.
- It can affect just one bone (monostotic form) or multiple bones (polyostotic form). Jaw involvement is common (especially the maxilla).
- Most common in adolescents and young adults.
- Clinical signs and symptoms: Painless, slow and progressive enlargement of the affected bone.
- Initially the lesion appears as an ill-defined radiolucency, but later fine trabeculae become gradual evident, resulting in a mixed appearance. As the lesion progresses the accumulation of the abnormal trabeculae is producing the typical “ground glass” or “orange peel” appearance.