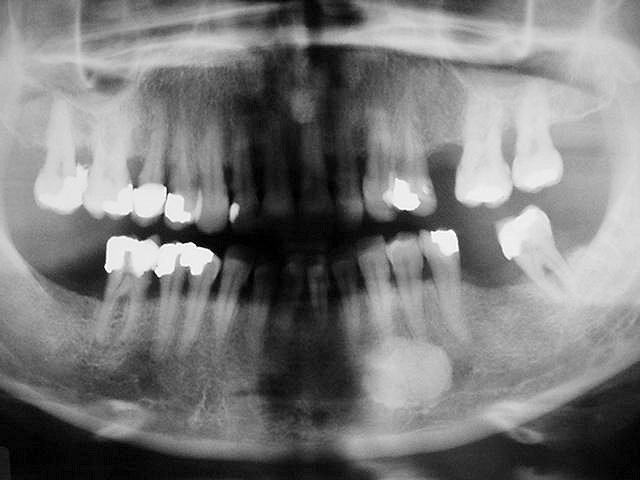
Osteoma and exostoses .
- Benign, slow-growing neoplasm of bone. Osteomas are divided in two types: Central and Peripheral.
- The mandible is affected more often than maxilla and the most frequent sites are: the lingual surface of the body and ramus, the condyle, the coronoid process and the inferior border.
- Osteomas are usually asymptomatic and most often are detected as incidental radiographic findings.
- Multiple osteomas may be found in patients with Gardner syndrome.