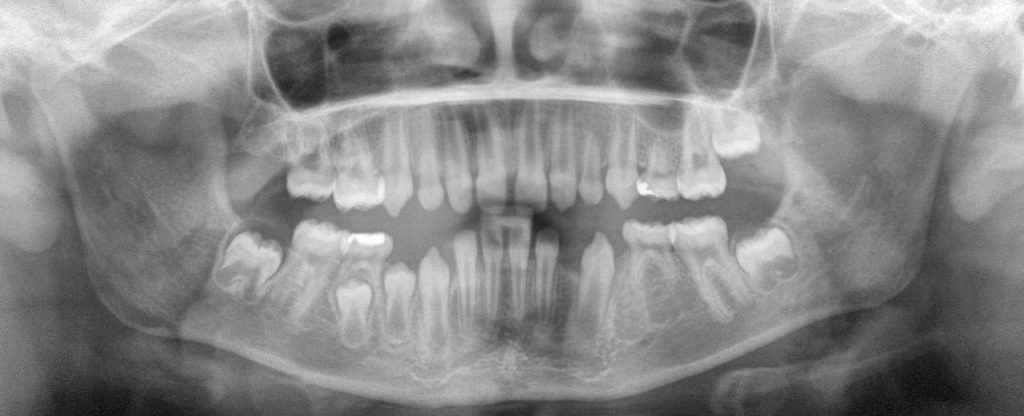
Number of teeth .
- Hypodontia or partial anodontia refers to less than 6 teeth missing in both jaws. The most commonly missing teeth are third molars followed by second premolars and maxillary lateral and mandibular central incisors. Hypodontia may related with Down’s syndrome.
- Oligodontia refers to more than 6 teeth missing in both jaws.
- Anodontia (total anodontia), is the absence of all teeth in both jaws and is extremely rare. Anodontia or oligodontia may occur in patients with ectodermal dysplasia.
- Hyperdontia or supernumerary teeth is the condition where one or more teeth develop, in addition to the normal dentition. When supernumerary teeth have normal morphologic features the term supplemental tooth is sometimes used. A mesiodens is a supernumerary tooth between the maxillary incisors. Hyperdontia may associated with specific syndromes such as: Cleidocranial Dysostosis and Gardner syndrome.