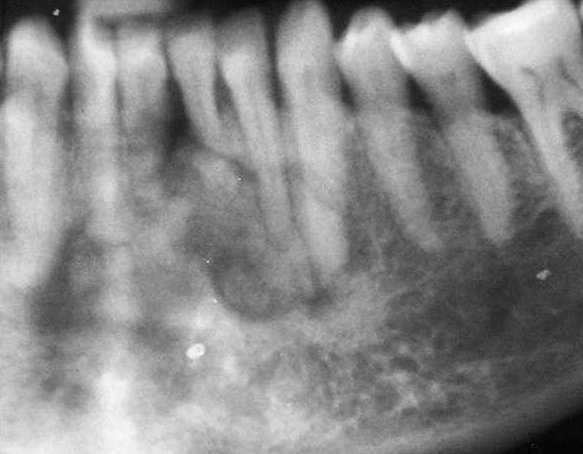
Cementoblastoma .
- Rare benign neoplasm. Most commonly in the second and third decade of life.
- Most common location: premolar / molar region of the mandible.
- Usually it is attached to the root of the affected tooth. Tooth displacement and root resorption are common findings.
- In 50% of cases there is pain and swelling.
- Three stages of development: radiolucent – mixed – radiopaque.
- When the lesion is radiopaque, it is usually surrounded by a thin radiolucent halo.