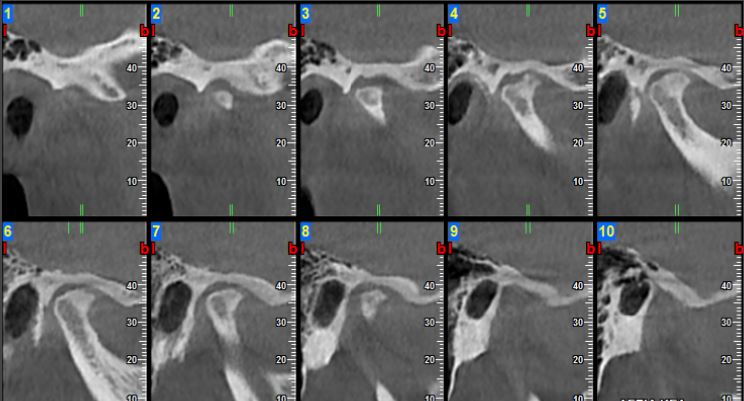
Osteoarthritis (degenerative arthritis) .
- TMJ osteoarthritis is the result of disc dislocation, trauma or functional overburden. The incidence increases with age and it normally starts from the age of 40. Osteoarthritis can also occur in young patients aged 20 to 40 years after an injury to the TMJ area.
- Female to male ratio is around 7:1.
- Symptoms: pain on palpation and movement, joint noises (crepitus), limitation of mouth opening , decreased range of motion and deviation in the jaw opening.
- Imaging features: flattening of the condyle, erosion of the condylar head and glenoid fossa, formation of osteophyte and reduced joint space. In advanced stages of the disease, sclerosis of the bone structures of the TMJ (condylar head, glenoid fossa and articular eminence), resorption of the condylar head and bone contact of the condyle with the glenoid fossa (with the mouth closed) and the condyle with the articular eminence (with the mouth open) can be seen.