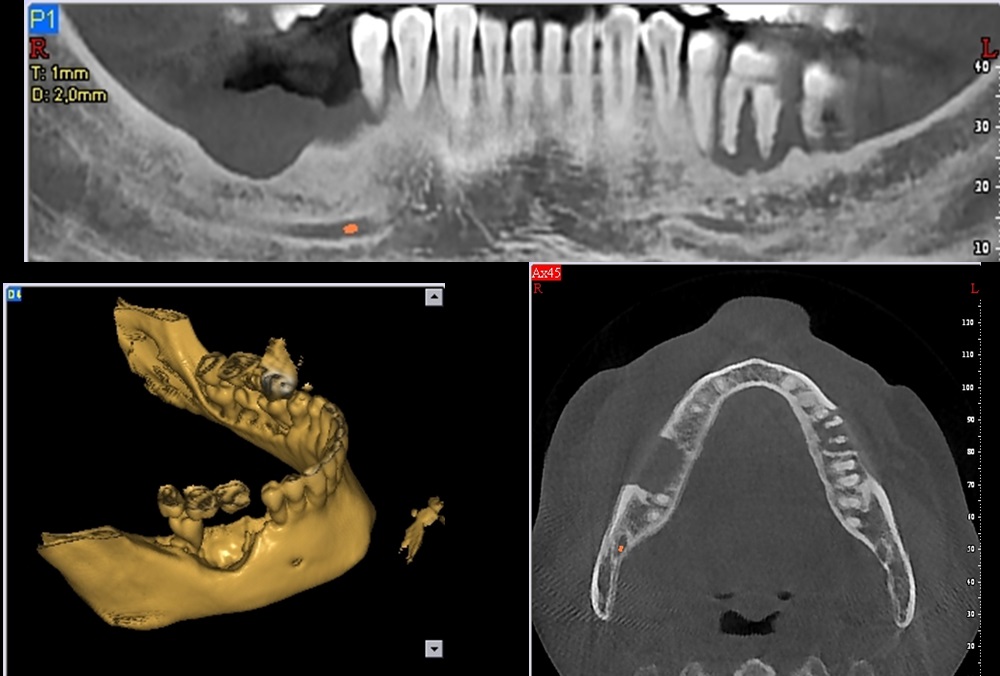
Squamous cell carcinoma .
- The most common malignant neoplasm of the oral cavity and jaw bones.
- The jaws are affected by peripheral infiltration when the tumor is located in the gingiva, the alveolar mucosa, the floor of the mouth and the hard palate.
- The radiographic findings depend on the degree of infiltration. Computed tomography is necessary to accurately determine bone invasion and destruction.
- Radiographically an ill defined, osteolytic radiolucency, is observed which initiates as peripheral bone erosion.
- The adjacent teeth are loosened (floating teeth) and the roots are laterally resorbed giving the characteristic picture of ‘nail end effect’.