Eosinophilic granuloma (Langerhans cell histiocytosis) .
- Osseous lesion that results from the abnormal proliferation of Langerhans cells.
- Eosinophilic granuloma is the non malignant, localized form of the disease.
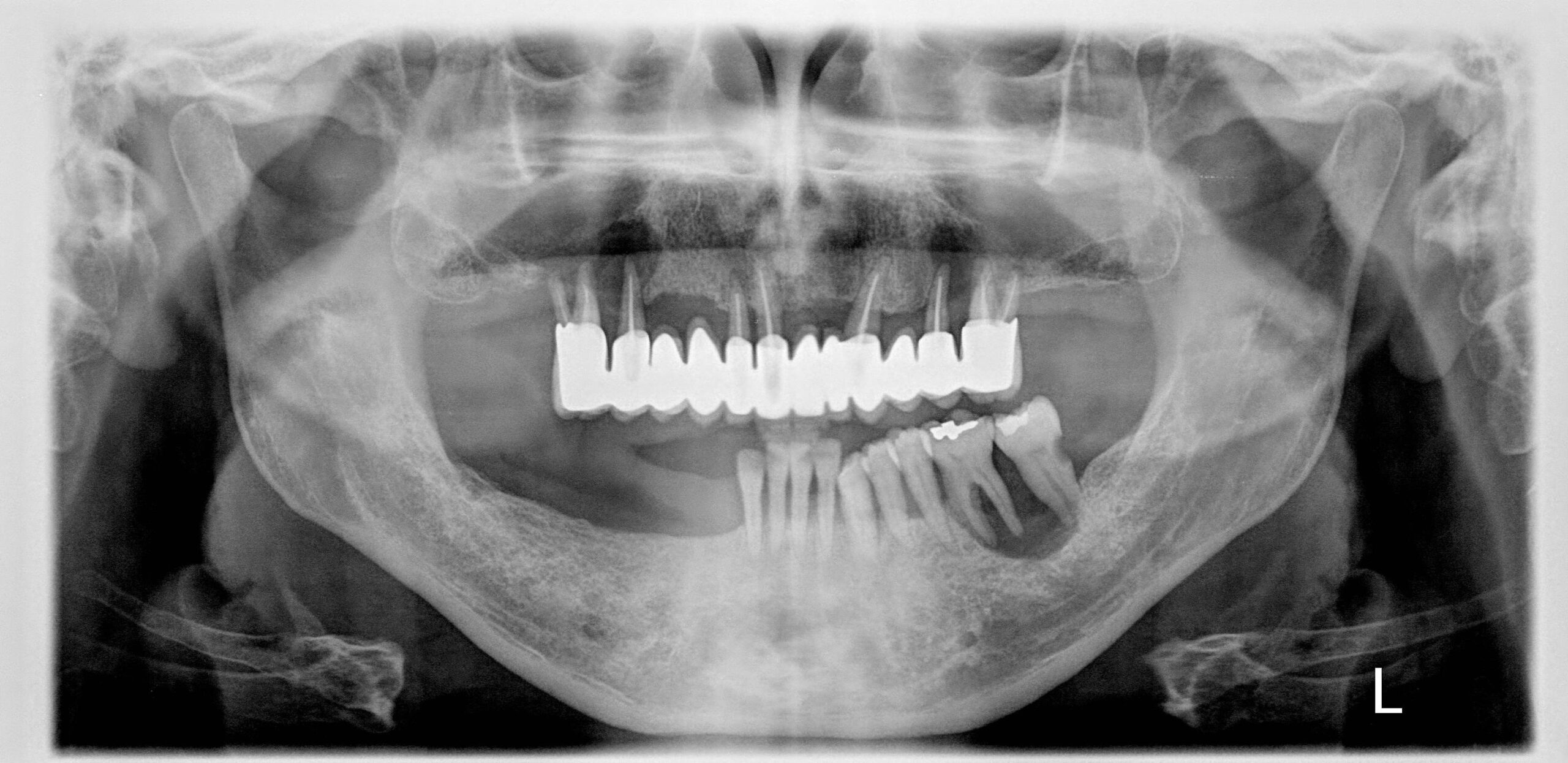
- The posterior part of the maxilla and the mandible are the most common locations when the disease affects the jaws. The lesions may be solitary or multiple and the involvement of the jaws is a relatively common finding.
- Radiographically eosinophilic granuloma appears as a periapical or inter radicular radiolucency with well or relatively ill defined borders. Most often the lesions are multiple with irregular or moth-eaten borders and cortical infiltration or destruction is observed.
- Clinically in some cases the condition resembles periodontal disease and teeth mobility or teeth loss are observed.
- Eosinophilic granuloma has a good prognosis after treatment but in some cases recurrence is observed.