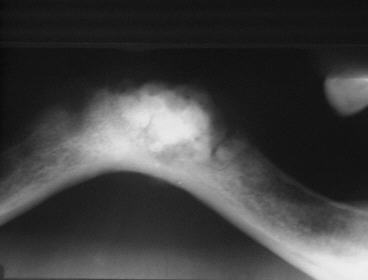
Sclerosing Osteomyelitis .
- It is a rare, chronic, non-pyogenic form of osteomyelitis that primarily affects the mandible. It is characterized by inflammation, sclerosis (hardening), and thickening of the bone due to a prolonged infection.
- Radiographically, it appears as a diffuse radiopacity with ill defined borders.