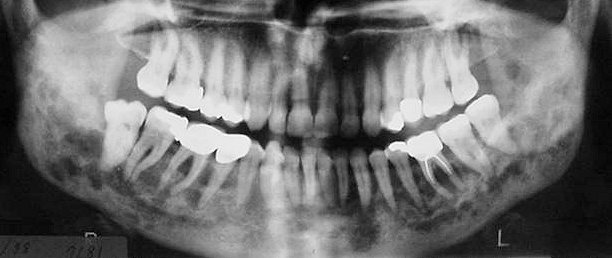
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (eosinophilic granuloma) .
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis includes three clinical forms:
- Eosinophilic granuloma: is the localized form of the disease (usually in children and young adults)
- Hand-Schuller-Christian: is the chronic, widespread form of the disease
- Leterrer-Siwe: is the malignant, acute and widespread form of the disease (children under 3 years old).
- Of the above clinical forms eosinophilic granuloma, whether single or multiple, is often found in the jaws.
- Most often the lesions are located either periapical or peri-radicular to the teeth and usually are misinterpreted as periapical granulomas and cysts or as periodontal disease.
- Radiographically the lesions are radiolucent with somewhat irregular or ill defined borders and have the tendency to extend deeper in the medullary bone.
- Computed tomography images, show perforation and destruction of the cortical plates or the floor of the nasal and maxillary sinus cavities. In a short period of time, loss of bony support, mobility or apoptosis of the adjacent teeth are observed.