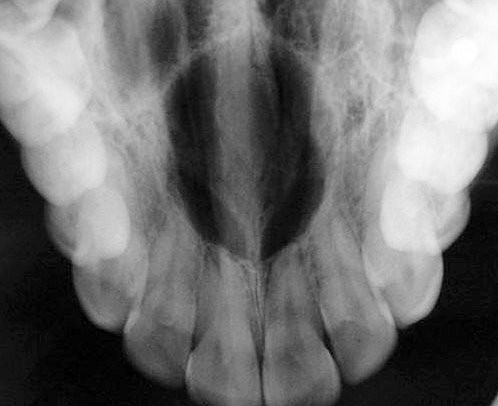
Nasopalatine duct cyst .
- The most common non-odontogenic cyst, which accounts for approximately 70-75% of all non-odontogenic cysts. It arises from epithelial remnants of the nasopalatine duct or incisive canal.
- It occurs at all ages, but most often between the ages of 40 and 60 years old.
- Its localization is characteristic, as it is always depicted between the roots of the central incisors of the maxilla.
- Radiographically, it appears as a well-circumscribed, unilocular, round or oval, radiolucency with corticated borders.
- It may cause displacement of adjacent teeth and very rarely root resorption. It may also cause palatal expansion.
- The prognosis is good. After surgical removal no recurrences occur.