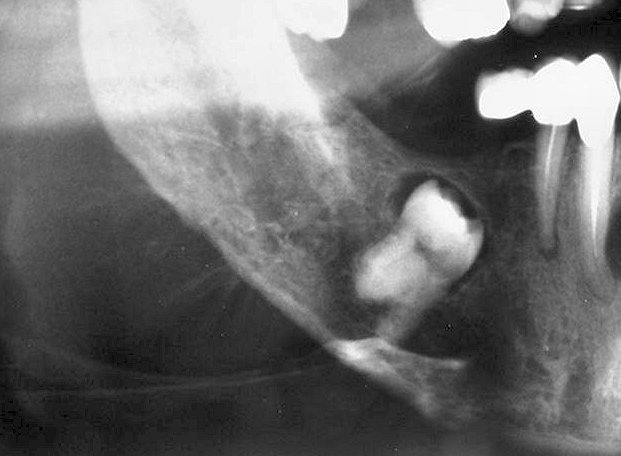
Osteogenic sarcoma (osteosarcoma) .
- The most common malignant tumor of the osseous tissue.
- The mean age of occurrence is 30-40 years. Maxilla and mandible are affected with the same proportion.
- Clinical manifestations: Pain and swelling of the involved bone, loose teeth, paresthesia, bleeding, nasal obstruction.
- An early radiographic finding is the widening of the periodontal ligament space.
- There are three main types:
- Osteolytic – no neoplastic bone formation: radiolucency with poorly defined or moth-eaten borders, loosening of the adjacent teeth.
- Mixed – patches of neoplastic bone formed within a poorly defined radiolucency with variable internal radiopacity.
- Osteosclerotic– neoplastic bone formation: Formation of sub-periosteal bone orientated at right angles to the cortex, producing the so-called ‘sun-ray appearance’, loosening of the adjacent teeth, distortion of the alveolar ridge.