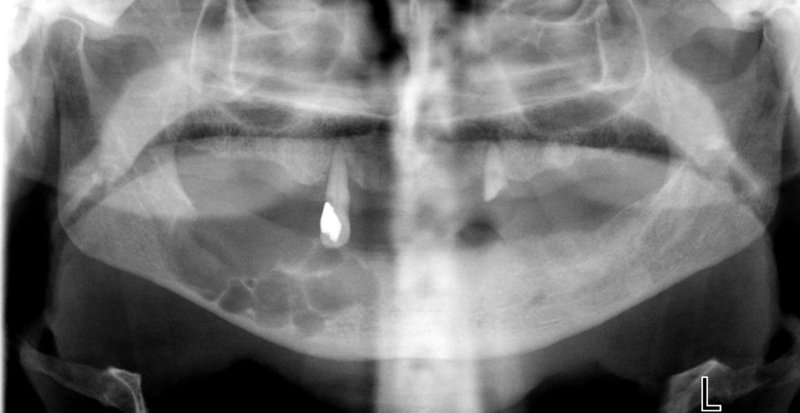
Odontogenic keratocyst (multilocular) .
- The characteristic feature of odontogenic keratocyst is that the epithelium lining the cystic cavity is keratinized or parakeratinized.
- Most common location: the posterior area of the mandible, the angle and the mandibular ramus.
- It may occur at any age but mostly develops during the second and third decades of life.
- The lesion may become large in size. It grows along the internal aspect of the jaws, causing thinning or even perforation of the cortical plates.
- Radiographically, small lesions are usually unilocular (often with scalloped margins), while larger lesions are multilocular with soap bubbles or honeycomb appearance.
- Odontogenic keratocyst has the tendency for recurrence after inadequate surgery.
- Adjacent teeth are usually vital and rarely resorbed.