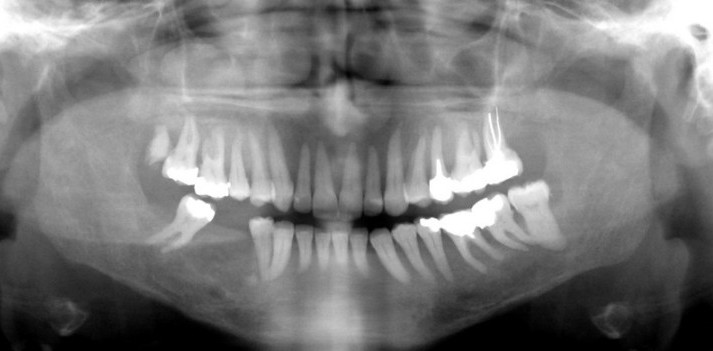
Hyperparathyroidism .
- Hyperparathyroidism is distinguished as primary and secondary. The increased secretion of parathyroid hormone causes generalized bone resorption (osteopenia), bone pain, pathological fractures and increased serum calcium levels.
- Thinning of cortical plates and resorption of the trabecular pattern (ground glass appearance).
- The skull bones become granular.
- Loss of lamina dura.
- Dilution of the lower border of the mandible. At a late stages, cyst-like radiolucencies are formed (brown tumors).
- After treatment, the bone pattern returns to normal.