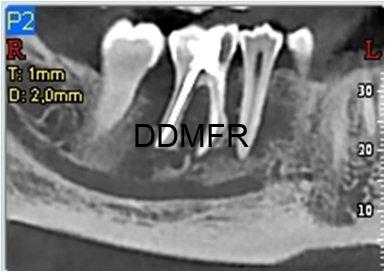
Osteomyelitis, periapical .
- It is an inflammatory process of the jaws which involves the bone marrow, the cortex and the periosteum. Dental infection is the most common etiologic factor.
- The acute phase of the suppurative osteomyelitis is rapid and shows no radiographic signs in the first 8-10 days.
- Without treatment, acute osteomyelitis may progress into a chronic phase with bone destruction.
- As the lesion progresses, an ill defined or moth-eaten radiolucency at the apex of the affected tooth is observed.
- In some cases scattered radiopacities within the lytic lesion become apparent due to bone sequestra.
- CT and CBCT scans, show perforations of the cortical plates and sometimes sub periosteal bone reaction.