Osteoporosis .
- The most common type of metabolic bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone density.
- It affects mostly women after menopause. High risk for pathological fractures.
- Generalized rarefaction, reduction of bone density, thinning of the inferior border of the mandible and erosions or heavy endosteal cortical residues of the endosteal margin of the cortical bone, are indications for osteoporosis.
- The most reliable method of diagnosing osteoporosis is the measurement of bone density with the DEXA method, where the percentage of bone loss is estimated.
Differential Diagnosis
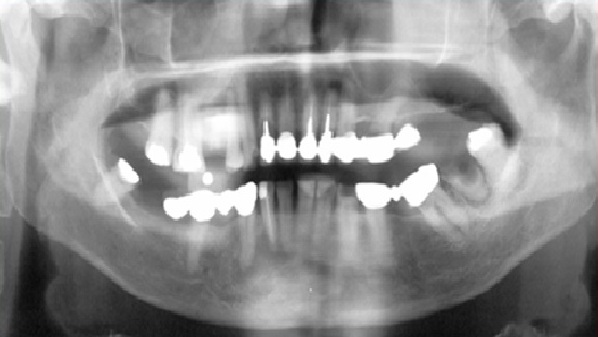
Case 1
Panoramic radiograph showing thinning of inferior border of the mandible.
Case 2
Panoramic radiograph of a female with osteoporosis showing heavy endosteal cortical residues of the endosteal margin of the cortical bone.
Case 3
CBCT of a female patient 78 years old, showing osteoporosis of the edentulous lower jaw.